 data removal services, stringent access controls, and regular audits to ensure compliance with privacy laws. Additionally, educating users about the risks and empowering them with tools to protect their personal identifiers is a critical step towards enhancing online security.
data removal services, stringent access controls, and regular audits to ensure compliance with privacy laws. Additionally, educating users about the risks and empowering them with tools to protect their personal identifiers is a critical step towards enhancing online security.
In conclusion, while the use of personal identifiers offers numerous benefits, it is vital to remain vigilant about the associated risks. By understanding these threats and advocating for robust protections, we can strive to maintain a balance between technological advancement and individual privacy rights.
Legal Frameworks Governing Biometric Use

This section delves into the regulatory structures that oversee the application of biological identifiers. It examines how various jurisdictions establish rules to balance technological advancements with individual rights, ensuring that the deployment of these technologies does not infringe upon personal liberties.
In many regions, legislative bodies have enacted specific laws to govern the collection, storage, and use of biological markers. These laws often require explicit consent from individuals before their unique identifiers can be utilized. They also mandate stringent security measures to prevent unauthorized access or misuse of these sensitive markers.
Moreover, the legal frameworks scrutinize the retention periods for these identifiers. They stipulate that once the purpose for which the identifiers were collected is fulfilled, they must be securely destroyed. This ensures that personal information is not retained longer than necessary, thereby reducing potential risks associated with data breaches.
Additionally, these regulations often include provisions for accountability. They hold entities that employ biological markers responsible for any breaches or misuse. This accountability mechanism serves as a deterrent against negligence and reinforces the importance of adhering to the established legal standards.
International cooperation is also a key aspect of these legal frameworks. As the use of biological identifiers often transcends national boundaries, international agreements and standards play a crucial role in harmonizing practices and ensuring a consistent level of protection for individuals worldwide.
In conclusion, the legal frameworks governing the use of biological identifiers are complex and multifaceted. They aim to foster innovation while safeguarding individual rights, ensuring that the benefits of technological advancements do not come at the expense of personal privacy and security.
Protecting Personal Biometric Information
In this section, we delve into the strategies and measures necessary to safeguard unique identifiers that individuals possess. The focus is on ensuring that these personal markers, which are integral to our identity, remain secure from unauthorized access and misuse.
Protecting such sensitive identifiers is crucial due to their irreplaceable nature and the profound impact their misuse can have on an individual’s life. Here are several key strategies to enhance the security of these personal markers:
- Encryption: Utilizing advanced encryption methods ensures that even if these identifiers are intercepted, they remain unreadable without the correct decryption keys.
- Access Controls: Implementing strict access controls limits who can view or use these identifiers, reducing the risk of unauthorized usage.
- Regular Updates: Keeping security protocols and software up-to-date helps in defending against newly discovered vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
- Awareness and Training: Educating users about the importance of protecting their unique identifiers and how to do so effectively is a fundamental step in prevention.
- Legal Protections: Establishing and enforcing laws that protect these identifiers from misuse provides a legal framework for accountability and recourse in cases of violation.
Additionally, it is essential to consider the ethical implications of collecting and storing these identifiers. Transparency about how they are used and ensuring consent from individuals are critical components of ethical data handling.
In conclusion, the protection of personal identifiers is a multifaceted challenge that requires a combination of technological, legal, and educational approaches. By implementing robust security measures and fostering a culture of awareness, we can significantly mitigate the risks associated with these sensitive markers.
Future Trends in Biometric Privacy
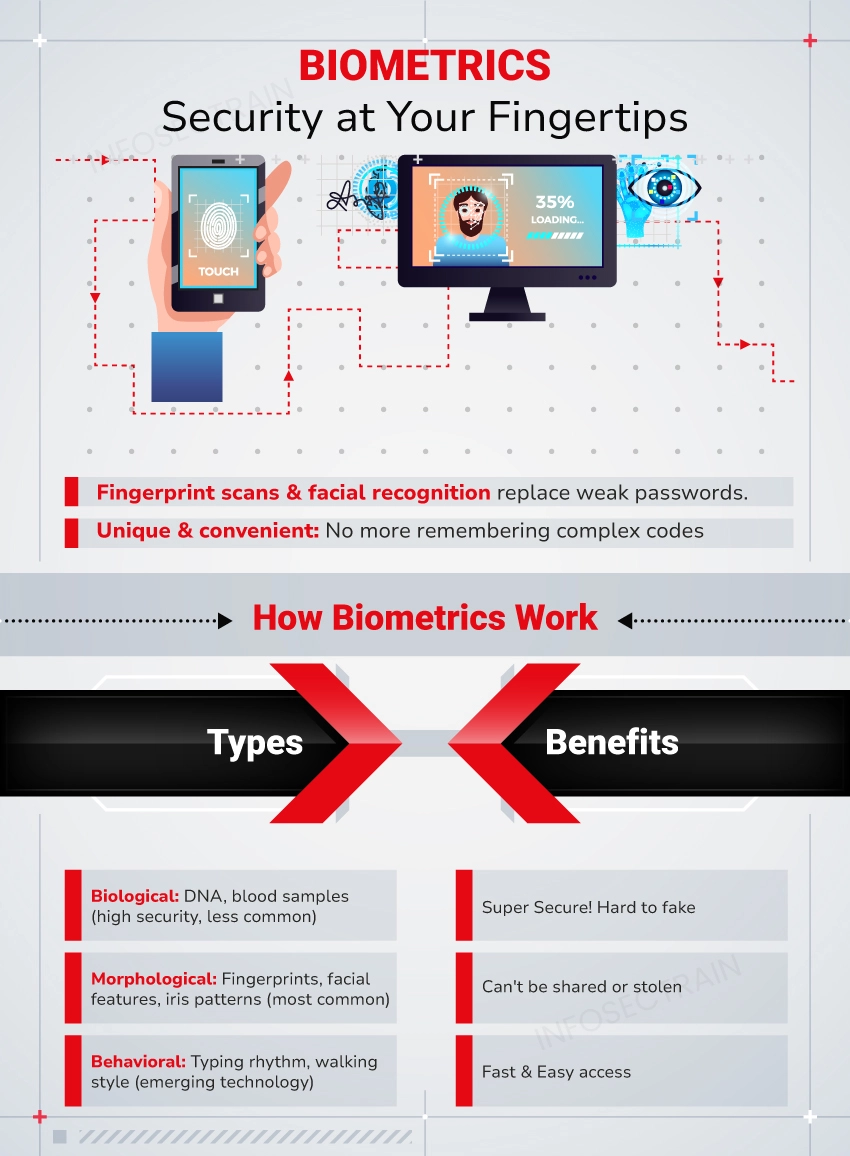
This section delves into the evolving landscape of personal identification safeguards, exploring how emerging technologies and regulations are shaping the protection of sensitive individual markers.
As we advance, the integration of advanced security measures with personal identification methods is expected to intensify. The focus will likely shift towards more sophisticated and less intrusive techniques, aiming to balance utility with respect for individual autonomy.
Emerging Technologies are at the forefront of these changes. For instance, the development of behavioral biometrics, which analyze patterns such as keystroke dynamics or gait, offers a promising alternative to traditional physical biometrics. These methods provide a higher level of security while potentially reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Moreover, the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the realm of personal identification is revolutionizing how we approach security. These technologies can enhance the accuracy of identification systems and adapt to new threats in real-time, making them invaluable tools in the ongoing battle against identity theft and fraud.
Regulatory Frameworks are also evolving to meet the challenges posed by these advancements. Governments and international bodies are increasingly recognizing the need for comprehensive legislation that addresses the ethical and legal implications of biometric technologies. This includes the protection of individual rights, such as the right to privacy and the right to control over one’s personal information.
In conclusion, the future of personal identification safeguards is likely to be characterized by a blend of technological innovation and robust legal protections. As we navigate these changes, it is crucial to ensure that the benefits of these technologies are realized without compromising the fundamental rights of individuals.

